What Is Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain
This excessive buildup of fluid can cause the ventricles to enlarge, leading to increased pressure on the brain tissue. The term “hydrocephalus” comes from the Greek words “hydro” meaning water and “cephalus” meaning head.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus can vary depending on the age of the individual and the rate of fluid buildup. In infants and young children, symptoms may include an enlarged head, rapid head growth, vomiting, sleepiness, irritability, and poor feeding
Hydrocephalus can be caused by:
- Premature birth
- Spina Bifida
- An infection such as meningitis
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Brain cysts or tumours
Hydrocephalus can occur at any point in a persons life and is most common in babies and the elderly. The effects of Hydrocephalus can also evolve and change over a person’s life time.
 How is Hydrocephalus Treated?
How is Hydrocephalus Treated?
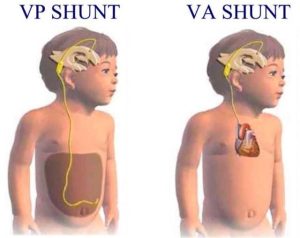
It is usually treated by the insertion of a Shunt. This can be a VP ( Ventriculoperitoneal ) or a VA ( Ventriculoatrial ) Shunt.
A VP Shunt drains the excess fluid into the stomach lining for reabsorbs while a VA drains into the atrium of the heart where it is then reabsorbed.
Failure of a shunt results in brain surgery.
 info@sbhi.ie
info@sbhi.ie  +353 (0)1 457 2329
+353 (0)1 457 2329 





